Note
Go to the end to download the full example code
Example: Holt-Winters Exponential Smoothing¶
In this example we show how to implement Exponential Smoothing. This is intended to be a simple counter-part to the Time Series Forecasting notebook.
The idea is that we have some times series
where we train on \(y_1, ..., y_T\) and predict for \(y_{T+1}, ..., y_{T+H}\), where \(T\) is the maximum training timestamp and \(H\) is the maximum number of future timesteps for which we want to forecast.
We will be using the update equations from the excellent book Forecasting Principles and Practice:
where
\(\hat{y}_t\) is the forecast at time \(t\);
\(h\) is the number of time steps into the future which we want to predict for;
\(l_t\) is the level, \(b_t\) is the trend, and \(s_t\) is the seasonality,
\(\alpha\) is the level smoothing, \(\beta^*\) is the trend smoothing, and \(\gamma\) is the seasonality smoothing.
\(k\) is the integer part of \((h-1)/m\) (this looks more complicated than it is, it just takes the latest seasonality estimate for this time point).
import argparse
import os
import time
import matplotlib
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import jax
from jax import random
import jax.numpy as jnp
import numpyro
from numpyro.contrib.control_flow import scan
from numpyro.diagnostics import hpdi
import numpyro.distributions as dist
from numpyro.infer import MCMC, NUTS, Predictive
matplotlib.use("Agg")
N_POINTS_PER_UNIT = 10 # number of points to plot for each unit interval
def holt_winters(y, n_seasons, future=0):
T = y.shape[0]
level_smoothing = numpyro.sample("level_smoothing", dist.Beta(1, 1))
trend_smoothing = numpyro.sample("trend_smoothing", dist.Beta(1, 1))
seasonality_smoothing = numpyro.sample("seasonality_smoothing", dist.Beta(1, 1))
adj_seasonality_smoothing = seasonality_smoothing * (1 - level_smoothing)
noise = numpyro.sample("noise", dist.HalfNormal(1))
level_init = numpyro.sample("level_init", dist.Normal(0, 1))
trend_init = numpyro.sample("trend_init", dist.Normal(0, 1))
with numpyro.plate("n_seasons", n_seasons):
seasonality_init = numpyro.sample("seasonality_init", dist.Normal(0, 1))
def transition_fn(carry, t):
previous_level, previous_trend, previous_seasonality = carry
level = jnp.where(
t < T,
level_smoothing * (y[t] - previous_seasonality[0])
+ (1 - level_smoothing) * (previous_level + previous_trend),
previous_level,
)
trend = jnp.where(
t < T,
trend_smoothing * (level - previous_level)
+ (1 - trend_smoothing) * previous_trend,
previous_trend,
)
new_season = jnp.where(
t < T,
adj_seasonality_smoothing * (y[t] - (previous_level + previous_trend))
+ (1 - adj_seasonality_smoothing) * previous_seasonality[0],
previous_seasonality[0],
)
step = jnp.where(t < T, 1, t - T + 1)
mu = previous_level + step * previous_trend + previous_seasonality[0]
pred = numpyro.sample("pred", dist.Normal(mu, noise))
seasonality = jnp.concatenate(
[previous_seasonality[1:], new_season[None]], axis=0
)
return (level, trend, seasonality), pred
with numpyro.handlers.condition(data={"pred": y}):
_, preds = scan(
transition_fn,
(level_init, trend_init, seasonality_init),
jnp.arange(T + future),
)
if future > 0:
numpyro.deterministic("y_forecast", preds[-future:])
def run_inference(model, args, rng_key, y, n_seasons):
start = time.time()
sampler = NUTS(model)
mcmc = MCMC(
sampler,
num_warmup=args.num_warmup,
num_samples=args.num_samples,
num_chains=args.num_chains,
progress_bar=False if "NUMPYRO_SPHINXBUILD" in os.environ else True,
)
mcmc.run(rng_key, y=y, n_seasons=n_seasons)
mcmc.print_summary()
print("\nMCMC elapsed time:", time.time() - start)
return mcmc.get_samples()
def predict(model, args, samples, rng_key, y, n_seasons):
predictive = Predictive(model, samples, return_sites=["y_forecast"])
return predictive(
rng_key, y=y, n_seasons=n_seasons, future=args.future * N_POINTS_PER_UNIT
)["y_forecast"]
def main(args):
# generate artifical dataset
rng_key, _ = random.split(random.PRNGKey(0))
T = args.T
t = jnp.linspace(0, T + args.future, (T + args.future) * N_POINTS_PER_UNIT)
y = jnp.sin(2 * np.pi * t) + 0.3 * t + jax.random.normal(rng_key, t.shape) * 0.1
n_seasons = N_POINTS_PER_UNIT
y_train = y[: -args.future * N_POINTS_PER_UNIT]
t_test = t[-args.future * N_POINTS_PER_UNIT :]
# do inference
rng_key, _ = random.split(random.PRNGKey(1))
samples = run_inference(holt_winters, args, rng_key, y_train, n_seasons)
# do prediction
rng_key, _ = random.split(random.PRNGKey(2))
preds = predict(holt_winters, args, samples, rng_key, y_train, n_seasons)
mean_preds = preds.mean(axis=0)
hpdi_preds = hpdi(preds)
# make plots
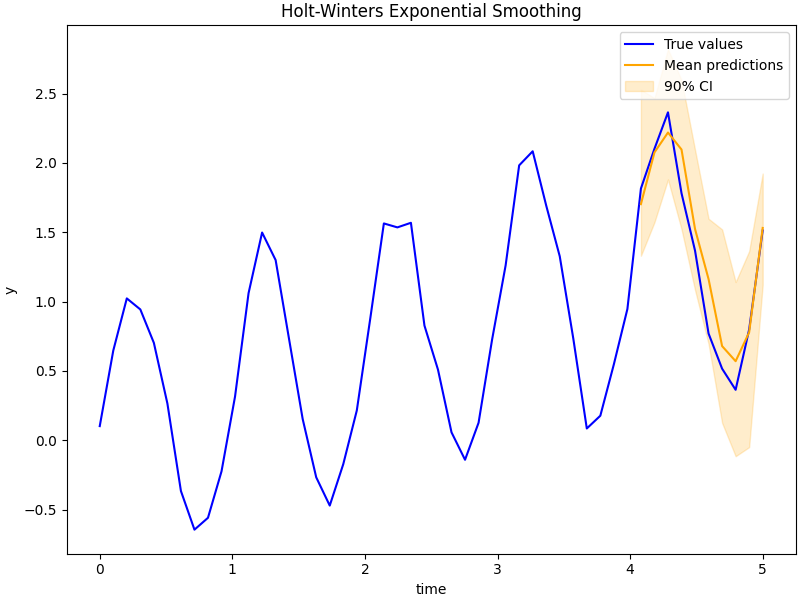
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(8, 6), constrained_layout=True)
# plot true data and predictions
ax.plot(t, y, color="blue", label="True values")
ax.plot(t_test, mean_preds, color="orange", label="Mean predictions")
ax.fill_between(t_test, *hpdi_preds, color="orange", alpha=0.2, label="90% CI")
ax.set(xlabel="time", ylabel="y", title="Holt-Winters Exponential Smoothing")
ax.legend()
plt.savefig("holt_winters_plot.pdf")
if __name__ == "__main__":
assert numpyro.__version__.startswith("0.14.0")
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description="Holt-Winters")
parser.add_argument("--T", nargs="?", default=6, type=int)
parser.add_argument("--future", nargs="?", default=1, type=int)
parser.add_argument("-n", "--num-samples", nargs="?", default=1000, type=int)
parser.add_argument("--num-warmup", nargs="?", default=1000, type=int)
parser.add_argument("--num-chains", nargs="?", default=1, type=int)
parser.add_argument("--device", default="cpu", type=str, help='use "cpu" or "gpu".')
args = parser.parse_args()
numpyro.set_platform(args.device)
numpyro.set_host_device_count(args.num_chains)
main(args)